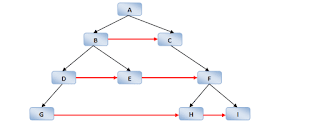
Print Binary Tree in 2-Dimensions
Find out the next neighbor of each node. If it is right node then print the null. Purpose of this algorithm is find out the garbage collector of data node.
package com.kartik.neighbor.print;
public class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right, neighbor;
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = neighbor = null;
}
}
- package com.kartik.neighbor.print;
public class BinaryTree {
int count = 5;
Node root;
// Sets the nextRight of root and calls connectRecur()
// for other nodes
void connect(Node node) {
// Set the nextRight for root
node.neighbor = null;
// Set the next right for rest of the nodes (other
// than root)
getNeighbor(node);
}
/*
* Set next right of all descendents of p. Assumption: node is a compete
* binary tree
*/
void getNeighbor(Node node) {
/*
* Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
*/
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Set the nextRight pointer for p's left child
if (node.left != null)
node.left.neighbor = node.right;
// Set the nextRight pointer for p's right child
// p.nextRight will be NULL if p is the right most child
// at its level
if (node.right != null)
node.right.neighbor = (node.neighbor != null) ? node.neighbor.left
: null;
String a = node.neighbor != null ? String.valueOf(node.neighbor.data)
: null;
System.out.println("nextRight of -->>>" + node.data + " is " + a);
// Set nextRight for other nodes in pre order fashion
getNeighbor(node.left);
getNeighbor(node.right);
}
// Function to print binary tree in 2D
// It does reverse inorder traversal
void print2DUtil(Node root, int space) {
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Increase distance between levels
space += count;
// Process right child first
print2DUtil(root.right, space);
// Print current node after space
// count
System.out.println("\n");
for (int i = count; i < space; i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println(root.data);
// Process left child
print2DUtil(root.left, space);
}
// Wrapper over print2DUtil()
void print2D(Node root) {
// Pass initial space count as 0
print2DUtil(root, 0);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Constructed binary tree is
15
7
14
3
13
6
12
1
11
5
2
9
4
8
*/
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
// tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.left.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.left.right = new Node(9);
// tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(11);
tree.root.right.left.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(13);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(15);
// Populates nextRight pointer in all nodes
tree.print2D(tree.root);
tree.connect(tree.root);
}
}
- Out Put:
15
7
14
3
13
6
12
1
11
5
2
9
4
8
nextRight of -->>>1 is null
nextRight of -->>>2 is 3
nextRight of -->>>4 is 5
nextRight of -->>>8 is 9
nextRight of -->>>9 is null
nextRight of -->>>5 is 6
nextRight of -->>>11 is 12
nextRight of -->>>3 is null
nextRight of -->>>6 is 7
nextRight of -->>>12 is 13
nextRight of -->>>13 is 14
nextRight of -->>>7 is null
nextRight of -->>>14 is 15
nextRight of -->>>15 is null