import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ZigZagTraversalMain<T> {
List<T> mainDisplay = new ArrayList<T>();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
public static boolean evenLevel = false;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void levelOrderQueue(T root) {
Queue<T> q = new LinkedList<T>();
int levelNodes = 0;
if (root == null)
return;
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
levelNodes = q.size();
list.clear();
while (levelNodes > 0) {
Node<?> n = (Node<?>) q.remove();
list.add((T) n.data);
if (n.left != null)
q.add((T) n.left);
if (n.right != null)
q.add((T) n.right);
levelNodes--;
}
if (evenLevel) {
System.out.print(list);
mainDisplay.addAll(list);
evenLevel = !evenLevel;
} else {
Collections.reverse(list);
mainDisplay.addAll(list);
System.out.print(list);
evenLevel = !evenLevel;
}
System.out.println("");
}
for (T t : mainDisplay) {
System.out.print(t+"-->");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception {
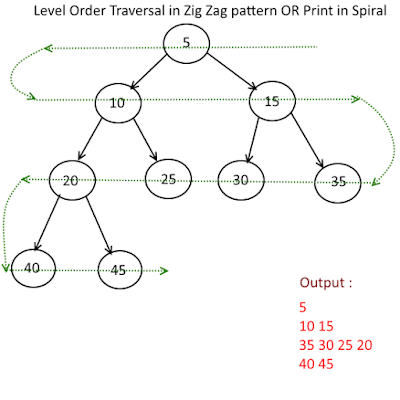
Node<Integer> root = new Node<Integer>(5);
root.left = new Node<Integer>(10);
root.right = new Node<Integer>(15);
root.left.left = new Node<Integer>(20);
root.left.right = new Node<Integer>(25);
root.right.left = new Node<Integer>(30);
root.right.right = new Node<Integer>(35);
root.left.left.left = new Node<Integer>(40);
root.left.left.right = new Node<Integer>(45);
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
ZigZagTraversalMain<Node> zig = new ZigZagTraversalMain<Node>();
System.out.println(" Spiral Print of a Tree : ");
zig.levelOrderQueue(root);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Node<String> stringRoot = new Node<String>("Kartik");
stringRoot.left = new Node<String>("Chandra");
stringRoot.right = new Node<String>("Mandal");
stringRoot.left.left = new Node<String>("West Bengal");
stringRoot.left.right = new Node<String>("Java");
stringRoot.right.left = new Node<String>("Unisys");
stringRoot.right.right = new Node<String>("Google");
stringRoot.left.left.left = new Node<String>("Man");
stringRoot.left.left.right = new Node<String>("Samsung");
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
ZigZagTraversalMain<Node> stringZig = new ZigZagTraversalMain<Node>();
System.out.println(" Spiral Print of a Tree For String: ");
stringZig.levelOrderQueue(stringRoot);
}
}
class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> left;
Node<T> right;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
Out put:
Spiral Print of a Tree :
[5]
[10, 15]
[35, 30, 25, 20]
[40, 45]
5-->10-->15-->35-->30-->25-->20-->40-->45-->
----------------------------------
Spiral Print of a Tree For String:
[Kartik]
[Chandra, Mandal]
[Google, Unisys, Java, West Bengal]
[Man, Samsung]
Kartik-->Chandra-->Mandal-->Google-->Unisys-->Java-->West Bengal-->Man-->Samsung-->
Explain
Better Solution :
Idea is to take all nodes at each level and print them forward and reverse order alternatively.
Create a ArrayList al.
Do the level order traversal using queue(Breadth First Search). Click here to know about
how to level order traversal.
For getting all the nodes at each level, before you take out a node from queue, store
the size of the queue in a variable, say you call it as levelNodes.
Now while levelNodes>0, take out the nodes and add it to the array list and add their
children into the queue.
Alternatively print the array list in forward and backward order.
After this while loop put a line break.
Time Complexity : O(N)